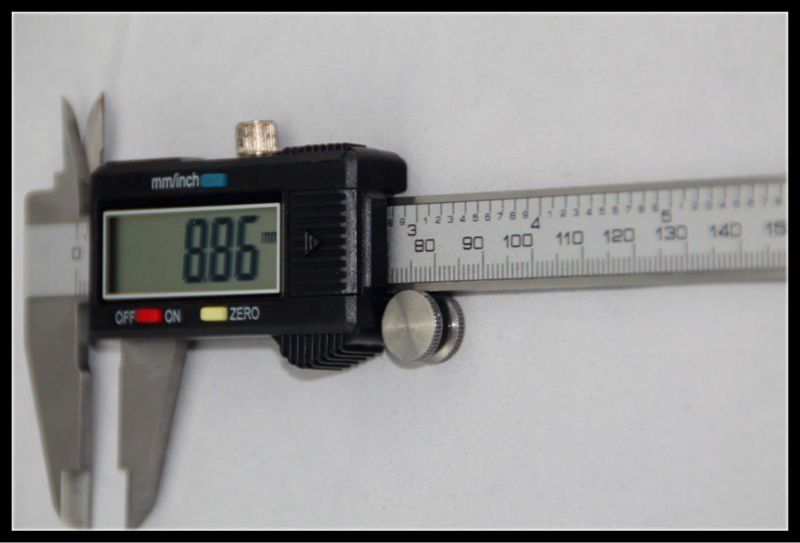
The session started by the facilitator going through the terminology of machining and these included;
# Milling - which means taking some materials off a certain piece done by machine like the CNC machine which are programmed to manufacture the required shape.
#Grinding - this is a process of rubbing off some materials to reduce size or diameters like crankshafts.
#Stamping - which is basically shearing the materials like sheets of metal to make holes through instead of using drill bits. Below is a picture of a bracket i stamped after cutting it on the Guillotine and then bending on the Sheet bender before cutting off excess length using a hand bench snipper.
In actual fact safety comes first, every machine has safety rules and regulations to follow before, during and after use. The facilitator then demonstrated with a round piece of polythene, by using the lathe to reduce the diameter of the rod and making fine threads on it. it was drilled on the other side which was not supported and the tail stock the supported the loose end when the length was increased from the chuck side. The tool post is where the cutting tools are mounted and it can be rotated so that different angles of cutting can be achieved.
Lathe Machine
Guilotine Machine.